
The big mistake, when a new laboratory reactors constructed, is the belief of a universal reactor, being able to produce every of single of trustful information. In fact, many key parameters are necessary to be carried out in specific experiment and equipment. Thus, the appropriate selection of laboratory in specified function is challenging task. It is required to be considered:
Laboratory reactor is not able to be completely simulated commercial-scale reactor due to many reasons. Many pieces of information are gathered in order to evaluate and extrapolate possibility of real performance of catalyst in acceptable range.
The generally operating conditions of laboratory reactor are recommended:
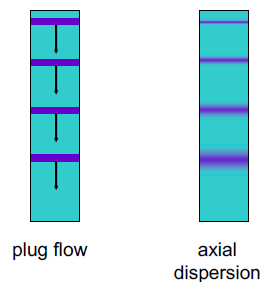
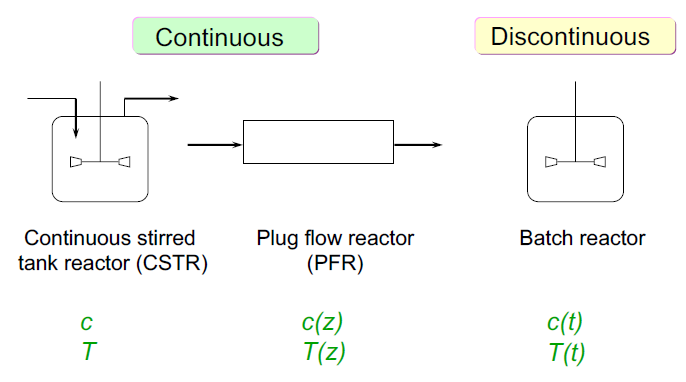
Laboratory reactors popularly used are “Continuously-stirred tank reactor (CSTR)” and “Plug-flow reactor (PFR)”, being strongly preferred over other reactors. Limitation of Batch reactor is uncouple the reaction kinetics from deactivation. Unreliable kinetic data is inaccurate if it is obtained from experiment carried out in complex hydrodynamics such as bubble-column or fluidized-bed reactor.
Recommendation
Many experts strongly recommend laboratory CSTR because: